YAML reference
The YAML file describes how an action behaves in Anchorpoint, registers it and can control Python scripts or command line applications. Each action needs a YAML file. The YAML file is declaratively described with key - value pairs.
# The action version
version: 1.0
# The action definition
action:
# name of the action
name: Batch Rename
# unique id
id: ap::rename
# Type can be either a cmd command or a python script
type: python
# Will be shown in the tooltip of the Action
description: Renames a set of selected files
# What is the icon that will be shown in the context menu. Use the Anchorpoint icon picker to get the path of the Anchorpoint icons.
icon:
path: :/icons/design-tools-photo-editing/pencil.svg
# The Python script that will be triggered
script: batch_rename.py
# In which area of the Anchorpoint desktop app will this action be placed
register:
# Place it in the file context menu
file:
enable: true
This example triggers a Python script that passes a selection of files to a batch renaming process.
Triggers in Anchorpoint
You can trigger actions from various places in the UI. To add triggers in the YAML file, scroll down to the "register" section.
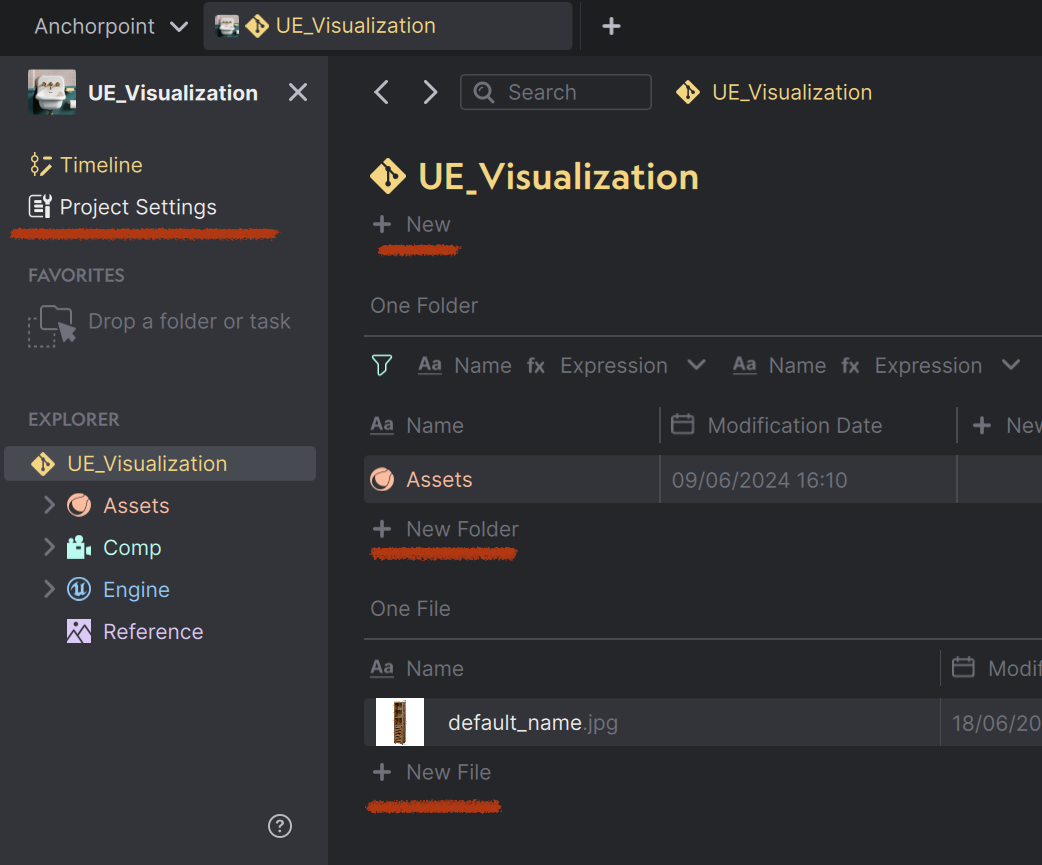 | Register actions for sidebar, new_task, new_folder and new_file. On the sidebar, the name of the action will appear as a button, for the "new" registrations, the buttons will appear each in a context menu. |
|---|---|
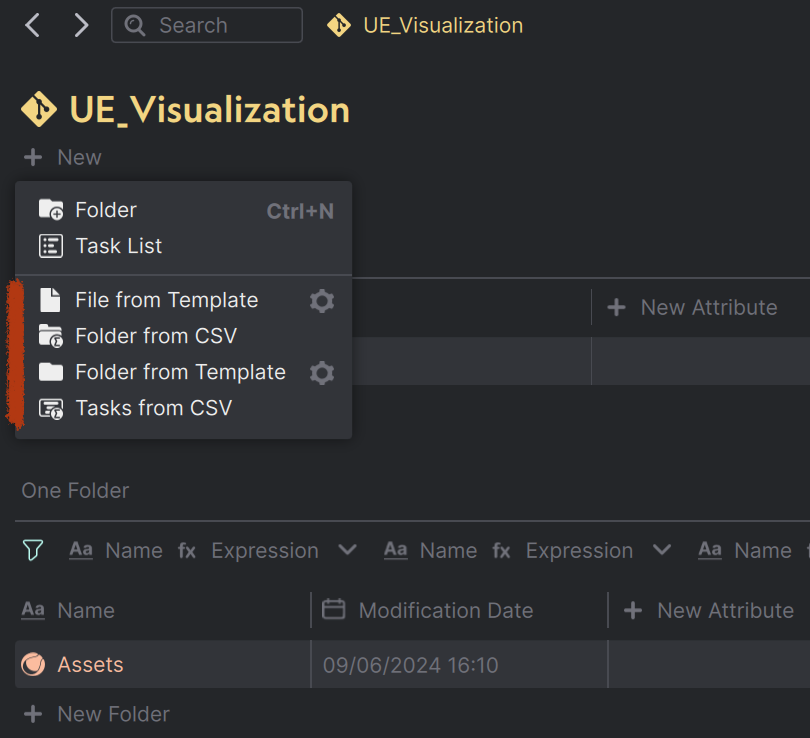 | Opening the context menu for new_task, new_folder and new_file. All the actions registered under these types, will be listed here. |
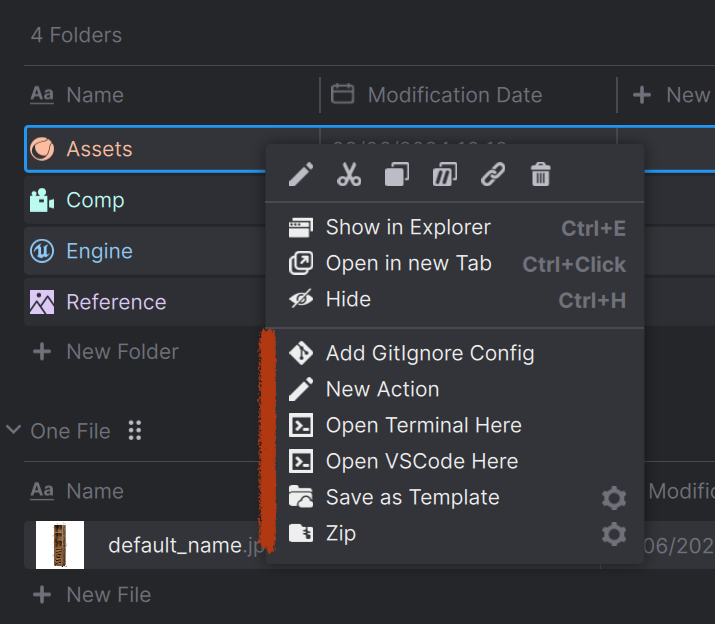 | Examples for a folder action, which will show up in the context menu of a folder. |
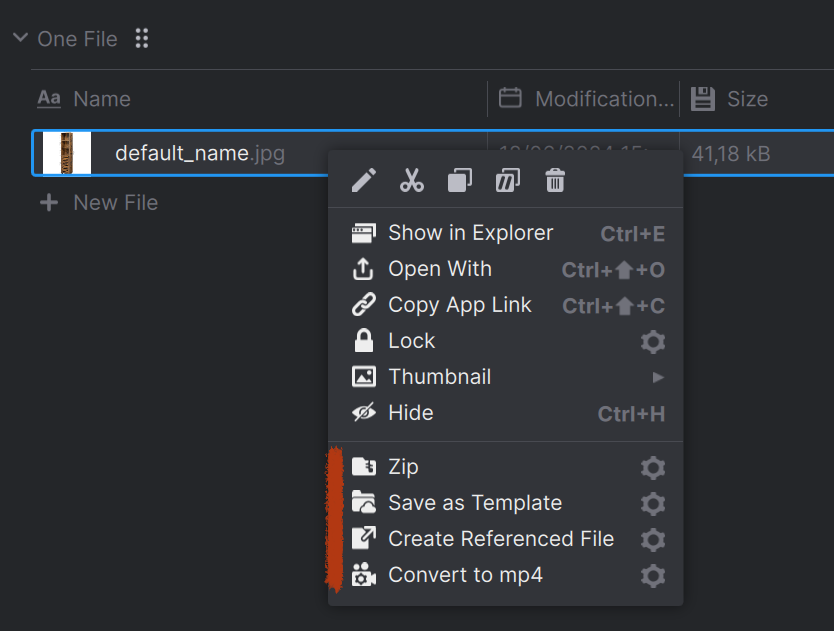 | Examples for registering the file action, which will show up in the context menu of a file. |
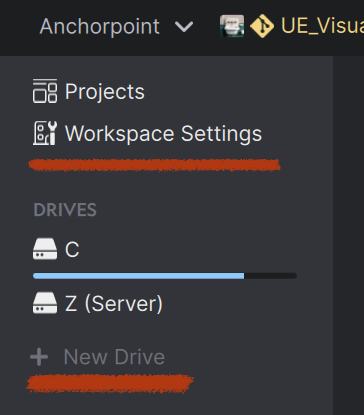 | Here you can register workspace_overview actions and new_drive actions. The drive register is an entry in the context menu when you do a right-click on a drive. |
Basic Keys
See the following list to learn about the basic keys that can be used to define your action.
version
A required property that sets the current action version.
# Required
version: 1.0
The following keys are subkeys of the action key.
name
Provides the name that shows up in Anchorpoint e.g. in the context menu
action:
#This will appear in the UI
name: "Convert Video to mp4"
id
A unique identifier. It is generally a good idea to provide a "namespace" for your action so that there is a lower chance to clash with Actions provided by other users.
action:
id: "ap::ffmpegConvertVideo"
type
What type of action, either "command", "python", or "package".
# Example for triggering a python script
action:
# The Python script that will be triggered
type: python
script: batch_rename.py
# Example for triggering an executable directly
action:
# In case an executable will be triggered
type: command
command: "ffmpeg.exe"
arguments: "-i ${path} ${root}/03_Export/Videos/yamlExample.mp4"
command
The path to the executable of a command line application like FFmpeg (e.g. ffmpeg.exe) if the action is of type "command". The path can be absolute or relative to the yaml file.
arguments
The variables to be passed to the command line application. In this example, instead of an absolute path, we take the $\{path\} variable, which returns us the file we selected in Anchorpoint.
We also use the $\{root\} variable, which gives us the path of the project.But this also means that this action can only be called in a project that contains a "03_Export/Videos" folder.
action:
type: command
command: ffmpeg.exe
arguments: "-i ${path} ${root}/03_Export/Videos/yamlExample.mp4"
script
The path to the Python script if the action is of type "python". It expects a Python 3.9 script. The path can be absolute or relative to the yaml file.
action:
type: python
script: save_as_template.py
author
Who created this action.
action:
author: "Anchorpoint Software GmbH"
description
What does your action do?.
action:
author: "Create a video from all files that are sharing the same suffix"
details
A detailed description of your action. Currently this is only used for packages. The content supports basic HTML.
action:
author: "Create a video from all files that are sharing the same suffix"
register
Specify where your action should be registered within Anchorpoint. Actions can be registered for the:
- file and folder context menu
- for the new file, folder, and drive buttons
- the left sidebar in the browser. Use the filter wildcard key to only register the action if the filter matches. Separate multiple filters with a semicolon.
register:
file:
filter: "*.png;*.exr" #Wildcard matching
folder:
filter: "*/assets/*"
new_file:
enable: true
new_folder:
filter: "*/shots/*"
new_task:
enable: true
drive:
enable: true
new_drive:
enable: true
sidebar:
enable: true
workspace_overview:
enable: true
Advanced Keys
This section handles more advanced YAML keys that can be used to specify how your action functions exactly.
inputs
A list of inputs for your action that can be defined in YAML and read in Python. Here it is worthwhile to store parameters, such as paths or certain settings, so that you don't have to modify your python script.
inputs:
URL: "anchorpoint.app"
target: ${root}/03_Export/Videos
You can also show basic prompts to ask the user for input. See more examples here.
inputs:
URL:
message: "What website do you like the most?"
default: "anchorpoint.app"
platforms
By default, actions are supported on all platforms. With the platforms key you can explicitly list the supported platforms:
platforms:
- win
- mac
python_packages
Anchorpoint ships with it's own Python interpreter to not depend on local installations. Hence, Anchorpoint is not using the locally installed python packages. Installing your own python packages for your actions is simple. Just specify your required packages in the action or packge YAML and Anchorpoint will install them, if needed.
python_packages:
- pillow
- opencv-python
toast
With the toast key you can control whether or not Anchorpoint shows a toast message on success or error. By default, Anchorpoint will show no message at all. In python you can fire up toasts directly.
toast:
success:
enable: false
error:
message: "Could not export file, please check your file system"
Variables
Within the YAML file you can access predefined and environment variables as well as defined inputs easily with the $\{var\} syntax.
inputs:
blender_path: "${BLENDER_DIR}/blender.exe" #environment variable BLENDER_DIR
command: ${blender_path}
arguments: --scene ${path} #access the predefined path variable
path
The absolute path to the file or folder.
inputs:
URL: "anchorpoint.app"
target: ${path}/ExportedFiles
relative_path
Path to the file or folder relative to the active project.
project_path
The project root folder.
inputs:
URL: "anchorpoint.app"
target: ${project_path}/03_Export/Videos
yaml_dir
The directory containing this YAML file.
action:
script: "${yaml_dir}/sbsToTextures.py"
folder
The active folder where you executed that action.
filename
The active filename without the path and without the suffix.
suffix
The suffix of the file, e.g. PNG.
Action Packages
An Action Package is a group of Actions bundled as a "feature". Action Packages are listed under "Workspace Settings / Actions" in the Anchorpoint desktop app. All default Anchorpoint actions are grouped via a package. You can package a set of actions in an action package. Action packages have 2 main advantages:
- They can be distributed using the Action Distribution System
- They can be enabled and disabled for the entire workspace
To define an action package set the type to package and provide a list of actions.
action:
#The package name
name: Batch Rename
id: ap::package::rename
# Mark it as a package type
type: package
# Should it be on/off per default
enable: false
# The description will be shown in the Action package list under Workspace Settings / Actions
description: A simple batch rename tool, that can be customized to your needs
# Package icon
icon:
path: batch_rename.svg
# List all the actions that are affected and will be enabled when the package is enabled
actions:
- ap::rename
# Restrict the action package for specific platforms
platforms:
- mac
- win
The YAML for a package features 2 main differences to a normal action YAML:
- The type is set to "package"
- A list of action ids is provided through the "actions" key
For workspace owners or administrators the packages show up in the Action settings for your workspace: