User Interface
The User Interface API provides comprehensive functionality for creating interactive dialogs, displaying notifications, and managing user interactions within Anchorpoint actions. This includes dialog creation with various input types, progress indicators, file browsers, and user feedback mechanisms.
Usage
Use the toast system
Using the toast system allows you to display messages to the users such as alerts, successes or errors.
import anchorpoint
# Get UI instance
ui = anchorpoint.UI()
# Show toast
ui.show_info("Process completed successfully")
ui.show_error("An error occurred", "Please check your input and try again")
Create a simple dialog
Build custom popup windows by adding new rows using methods in the dialog class. You can also add "columns" to your dialog by chaining UI elements such as dialog.add_text("First Row: ").add_input().
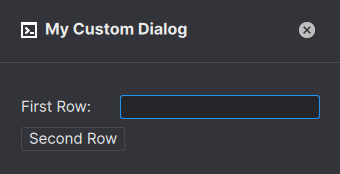
import anchorpoint
# Create and show a simple dialog
dialog = anchorpoint.Dialog()
dialog.title = "My Custom Dialog"
dialog.add_text("First Row: ").add_input()
dialog.add_button("Second Row")
dialog.show()
UI Class
Constructor
anchorpoint.UI()The UI class provides methods for user notifications, navigation, and browser interactions.
Methods
-
show_info(title, description="", duration=4000)Shows an info toast message within Anchorpoint.Arguments
title(str): The title of the toastdescription(str, optional): The description of the toastduration(int, optional): The duration (in ms) the toast is shown to the user
-
show_success(title, description="", duration=4000)Shows a success toast message within Anchorpoint.Arguments
title(str): The title of the toastdescription(str, optional): The description of the toastduration(int, optional): The duration (in ms) the toast is shown to the user
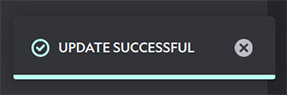 Shows a toast using a teal color scheme
Shows a toast using a teal color scheme -
show_error(title, description="", duration=4000)Shows an error toast message within Anchorpoint.Arguments
title(str): The title of the toastdescription(str, optional): The description of the toastduration(int, optional): The duration (in ms) the toast is shown to the user
-
show_system_notification(title, message, callback=None, path_to_image=None)Shows a notification on the operating system.Arguments
title(str): The title of the system notificationmessage(str): The message of the system notificationcallback(function, optional): A callback triggered when the notification is clickedpath_to_image(str, optional): Optional file path to an image displayed in the notification
-
navigate_to_file(file_path)Navigates the Anchorpoint browser to the provided file path.Arguments
file_path(str): The file to navigate to
-
navigate_to_folder(folder_path)Navigates the Anchorpoint browser to the provided folder path.Arguments
folder_path(str): The folder to navigate into
-
show_console()Shows the command console to the user. -
clear_console()Clears the console. -
reload()Reloads the current view of the Anchorpoint browser.
Dialog Class
Constructor
anchorpoint.Dialog()The Dialog class provides a flexible framework for creating custom user interfaces with various input controls and layouts. Alladd_*methods return the Dialog instance for method chaining.
Properties
title(str): Title displayed in the dialog window. Sets the main heading for the dialog.icon(str): Path or identifier for the dialog icon. Displayed alongside the title.
Methods
Layout and Structure
-
add_text(text)Adds a text label to the dialog.Arguments
text(str): Text content to display
Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
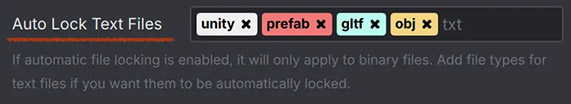 Adds a text field. Basic HTML formatting such as "
Adds a text field. Basic HTML formatting such as "<b>" or "<br>" is supported. This example uses it as a label for a tag input usingmy_dialog.add_text("Auto Lock Text Files").add_tag_input() -
add_empty()Adds vertical spacing between elements.Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
 Adds an empty space
Adds an empty space -
add_info(text)Adds an informational text block with distinctive styling.Arguments
text(str): Information text to display (supports HTML formatting)
Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
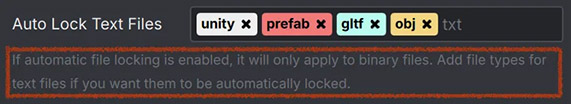 Adds a greyed out text field. Basic HTML formatting such as "
Adds a greyed out text field. Basic HTML formatting such as "<b>" or "<br>" is supported.
Input Controls
-
add_input(default="", placeholder="", callback=None, var=None, enabled=True, browse=None, browse_path=None, password=False, width=200, validate_callback=None)Adds a text input field to the dialog.Arguments
default(str, optional): Default value for the inputplaceholder(str, optional): Placeholder text shown when emptycallback(function, optional): Function called when input changesvar(str, optional): Variable name for retrieving the valueenabled(bool, optional): Whether the input is enabled (default: True)browse(class: BrowseType, optional): Add browse button for file/folder selectionbrowse_path(str, optional): Initial browse pathpassword(bool, optional): Whether to hide input text (default: False)width(int, optional): Width of the input field (default: 200)validate_callback(function, optional): Function for input validation
Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
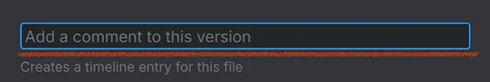 Adds a text input field. In case of selecting a folder or a file you can also add a browse button, which will open up the system's file browser.
Adds a text input field. In case of selecting a folder or a file you can also add a browse button, which will open up the system's file browser. -
add_dropdown(default, values, callback=None, var=None, enabled=True, filterable=False, validate_callback=None)Adds a dropdown selection control.Arguments
default(str): Default selected valuevalues(list of str or DropdownEntry): Available optionscallback(function, optional): Function called when selection changesvar(str, optional): Variable name for retrieving the selected valueenabled(bool, optional): Whether the dropdown is enabled (default: True)filterable(bool, optional): Whether users can filter options by typing (default: False)validate_callback(function, optional): Function for validating selection
Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
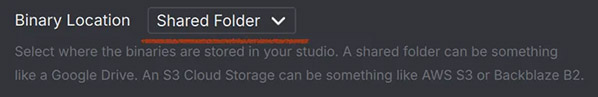 Adds a dropdown button where the user can select a pre defined entry
Adds a dropdown button where the user can select a pre defined entry -
add_checkbox(default=False, callback=None, var=None, enabled=True, text="")Adds a checkbox control.Arguments
default(bool, optional): Initial checked state (default: False)callback(function, optional): Function called when state changesvar(str, optional): Variable name for retrieving the valueenabled(bool, optional): Whether the checkbox is enabled (default: True)text(str, optional): Label text displayed next to checkbox
Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
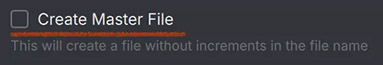 Adds a basic checkbox with a description
Adds a basic checkbox with a description -
add_switch(default=False, callback=None, var=None, enabled=True, text="")Adds a switch control (similar to checkbox but different styling).Arguments
default(bool, optional): Initial switch state (default: False)callback(function, optional): Function called when state changesvar(str, optional): Variable name for retrieving the valueenabled(bool, optional): Whether the switch is enabled (default: True)text(str, optional): Label text displayed next to switch
Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
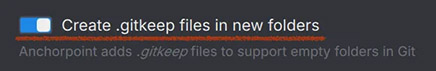 Adds a switch with a description
Adds a switch with a description
Action Controls
-
add_button(text, callback=None, var=None, enabled=True, primary=True)Adds an action button to the dialog.Arguments
text(str): Button label textcallback(function, optional): Function called when button is clickedvar(str, optional): Variable name for the buttonenabled(bool, optional): Whether the button is enabled (default: True)primary(bool, optional): Whether this is a primary button (default: True)
Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
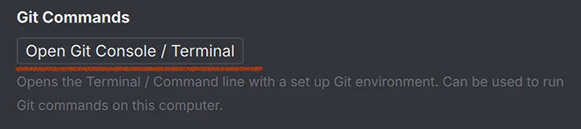 Adds a button. This one has set
Adds a button. This one has set primary=False.
Additional Controls
-
add_separator()Adds a visual separator line to the dialog.Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
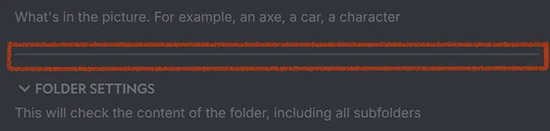 Adds a basic line for visual separation
Adds a basic line for visual separation -
add_image(path, var=None, width=300)Adds an image to the dialog.Arguments
path(str): Path to the image filevar(str, optional): Variable name for the imagewidth(int, optional): Width of the image (default: 300)
Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
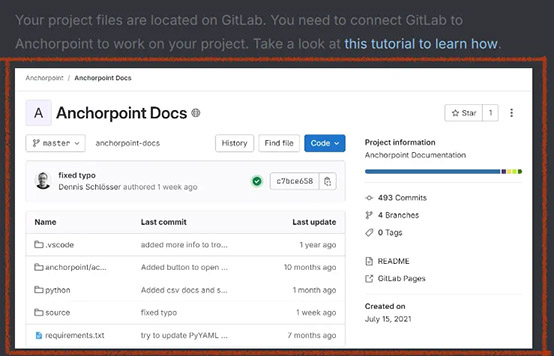 Adds an image. The height will be proportional to the width.
Adds an image. The height will be proportional to the width. -
add_tag_input(values, placeholder=None, callback=None, var=None, enabled=True, width=300)Adds a tag input control for multiple selections.Arguments
values(list of str): Available tag valuesplaceholder(str, optional): Placeholder textcallback(function, optional): Function called when tags changevar(str, optional): Variable name for retrieving valuesenabled(bool, optional): Whether the input is enabled (default: True)width(int, optional): Width of the input (default: 300)
Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
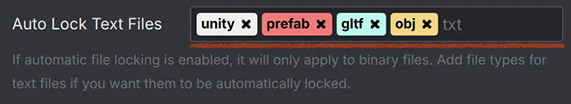 A tag input can be used for filtering file types or adding keywords
A tag input can be used for filtering file types or adding keywords
Organization
-
start_section(text, foldable=True, folded=True, enabled=True)Begins a collapsible section for grouping related controls.Arguments
text(str): Section header textfoldable(bool, optional): Whether section can be collapsed (default: True)folded(bool, optional): Whether section is folded by default (default: True)enabled(bool, optional): Whether the section is enabled (default: True)
Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
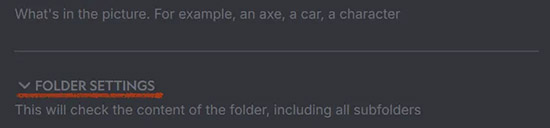 Adds a section that can show or hide interface elements. You always need to use
Adds a section that can show or hide interface elements. You always need to use end_section()at the end of the interface group. -
end_section()Ends the current section.Returns (class: Dialog): Returns self for method chaining
Dialog Management
-
show()Displays the dialog to the user. -
close()Closes the dialog. -
get_value(var)Retrieves the current value of a named control.Arguments
var(str): Variable name of the control
Returns The current value of the control (type depends on control type)
-
set_enabled(var, enabled)Enables or disables a control.Arguments
var(str): Variable name of the controlenabled(bool): Whether the control should be enabled
Examples
Basic Dialog Creation
import anchorpoint
def create_simple_dialog():
dialog = anchorpoint.Dialog()
dialog.title = "File Processor"
dialog.icon = ":/icons/action.svg"
# Add form elements
dialog.add_text("Select processing options:")
dialog.add_dropdown("Medium", ["Low", "Medium", "High"], var="quality")
dialog.add_checkbox(True, var="backup", text="Create backup")
dialog.add_input("output_", placeholder="Enter prefix", var="prefix")
# Add action buttons
dialog.add_button("Process", callback=process_files, var="process")
dialog.add_button("Cancel", callback=lambda d: d.close(), primary=False)
dialog.show()
def process_files(dialog):
quality = dialog.get_value("quality")
backup = dialog.get_value("backup")
prefix = dialog.get_value("prefix")
print(f"Processing with quality: {quality}, backup: {backup}, prefix: {prefix}")
dialog.close()
create_simple_dialog()
A dialog that shows a text label, a dropdown, a checkbox and an input each in a new row. The process_files is a callback that is triggered once the user clicks on the "Process" button. It reads the values from the input fields which the user has edited.
File Selection and Processing
import anchorpoint
import os
def file_conversion_dialog():
# Show file selection dialog using browse input
dialog = anchorpoint.Dialog()
dialog.title = "Image Conversion Setup"
# File selection with browse button
dialog.add_text("Select input file:")
dialog.add_input("", placeholder="Select image file", var="input_file",
browse=anchorpoint.BrowseType.File)
dialog.add_text("Select output folder:")
dialog.add_input("", placeholder="Select output folder", var="output_folder",
browse=anchorpoint.BrowseType.Folder)
# Conversion settings
dialog.add_separator()
dialog.add_text("Conversion Settings:")
dialog.add_dropdown("JPEG", ["JPEG", "PNG", "TIFF"], var="format")
dialog.add_dropdown("100%", ["25%", "50%", "75%", "100%"], var="scale")
dialog.add_checkbox(False, var="watermark", text="Apply watermark")
dialog.add_button("Convert", callback=convert_image)
dialog.add_button("Cancel", callback=lambda d: d.close(), primary=False)
dialog.show()
def convert_image(dialog):
input_file = dialog.get_value("input_file")
output_folder = dialog.get_value("output_folder")
format_type = dialog.get_value("format")
scale = dialog.get_value("scale")
watermark = dialog.get_value("watermark")
ui = anchorpoint.UI()
# Validate inputs
if not input_file or not output_folder:
ui.show_error("Missing Input", "Please select both input file and output folder")
return
try:
# Simulate image processing
print(f"Converting {input_file} to {format_type} at {scale} scale")
if watermark:
print("Applying watermark")
ui.show_success("Conversion Complete", f"Image saved to {output_folder}")
dialog.close()
except Exception as e:
ui.show_error("Conversion Failed", str(e))
file_conversion_dialog()
A dialog that also adds interface elements each in a new row. In the input field, the user can browse to a folder which is then validated in the callback. By the end, a toast is shown.
Advanced Dialog with Sections
import anchorpoint
def advanced_settings_dialog():
dialog = anchorpoint.Dialog()
dialog.title = "Advanced Processing Settings"
dialog.icon = ":/icons/settings.svg"
# Input Settings Section
dialog.start_section("Input Settings", folded=False)
dialog.add_input("", placeholder="Select source folder", var="source",
browse=anchorpoint.BrowseType.Folder)
dialog.add_input("*.jpg;*.png", placeholder="File filter", var="filter")
dialog.add_checkbox(True, var="recursive", text="Include subfolders")
dialog.end_section()
# Processing Options Section
dialog.start_section("Processing Options")
dialog.add_dropdown("Balanced", ["Fast", "Balanced", "Quality"], var="mode")
dialog.add_checkbox(False, var="metadata", text="Preserve metadata")
dialog.add_dropdown("4", ["1", "2", "4", "8"], var="threads")
dialog.end_section()
# Output Settings Section
dialog.start_section("Output Settings")
dialog.add_input("", placeholder="Select output folder", var="output",
browse=anchorpoint.BrowseType.Folder)
dialog.add_input("processed_", placeholder="Filename prefix", var="prefix")
dialog.add_checkbox(True, var="overwrite", text="Overwrite existing")
dialog.end_section()
# Action buttons
dialog.add_empty()
dialog.add_button("Start Processing", callback=start_processing, primary=True)
dialog.add_button("Cancel", callback=lambda d: d.close(), primary=False)
dialog.show()
def start_processing(dialog):
# Collect all settings
settings = {
'source': dialog.get_value("source"),
'filter': dialog.get_value("filter"),
'recursive': dialog.get_value("recursive"),
'mode': dialog.get_value("mode"),
'metadata': dialog.get_value("metadata"),
'threads': dialog.get_value("threads"),
'output': dialog.get_value("output"),
'prefix': dialog.get_value("prefix"),
'overwrite': dialog.get_value("overwrite")
}
# Validate settings
if not settings['source'] or not settings['output']:
ui = anchorpoint.UI()
ui.show_error("Invalid Settings", "Please select both source and output folders")
return
dialog.close()
# Start processing with progress
process_with_progress(settings)
def process_with_progress(settings):
import time
# Create progress indicator
progress = anchorpoint.Progress("Processing Files", "Starting processing...",
infinite=False, cancelable=True)
try:
steps = ["Scanning files", "Processing images", "Applying filters", "Saving results"]
for i, step in enumerate(steps):
if progress.canceled:
print("Processing cancelled by user")
break
progress.set_text(step)
progress.report_progress((i + 1) / len(steps))
print(f"Step {i+1}: {step}")
time.sleep(2) # Simulate work
if not progress.canceled:
ui = anchorpoint.UI()
ui.show_success("Processing Complete",
f"All files processed and saved to {settings['output']}")
finally:
progress.finish()
advanced_settings_dialog()
This example organizes interface elements into sections (into foldable groups) and uses a process indicator at the end that can be used for a heavy operation. Note that in practice you would run this process asynchronously.
Dynamic Dialog Updates
import anchorpoint
def dynamic_dialog_example():
dialog = anchorpoint.Dialog()
dialog.title = "Dynamic Settings"
# Initial form
dialog.add_text("Select media type:")
dialog.add_dropdown("Image", ["Image", "Video", "Audio"], var="type", callback=update_options)
dialog.add_text("Select format:")
dialog.add_dropdown("JPEG", ["JPEG", "PNG", "TIFF", "BMP"], var="format")
dialog.add_text("Output path:")
dialog.add_input("", placeholder="Enter output path", var="output")
dialog.add_button("Process", callback=process_media, var="process", enabled=False)
dialog.add_button("Cancel", callback=lambda d: d.close(), primary=False)
dialog.show()
def update_options(dialog, value):
# This is a simplified example showing the concept
# In practice, dynamic updates require more complex handling
format_options = {
"Image": ["JPEG", "PNG", "TIFF", "BMP"],
"Video": ["MP4", "AVI", "MOV", "MKV"],
"Audio": ["MP3", "WAV", "FLAC", "AAC"]
}
# Get current type
media_type = value
formats = format_options.get(media_type, [])
print(f"Available formats for {media_type}: {formats}")
# Enable process button once type is selected
dialog.set_enabled("process", True)
def process_media(dialog):
media_type = dialog.get_value("type")
format_type = dialog.get_value("format")
output = dialog.get_value("output")
ui = anchorpoint.UI()
if not format_type or not output:
ui.show_error("Incomplete Settings", "Please select format and output path")
return
ui.show_info("Processing Started", f"Converting to {format_type} format")
dialog.close()
dynamic_dialog_example()
This dialog enables/disables the "Process" button when a value is selected using the callback function update_options.